Data Communication Tutorial
Data communication plays an important role in today’s interconnected world and enables the exchange of information between devices and networks. Whether you’re sending an email, making a video call, or browsing the web, data communication ensures that information flows smoothly.
This Data Communication tutorial is designed for both beginners and experienced professionals, covering basic and advanced concepts of data communication. It includes topics such as the basics of data communication, OSI Model, TCP/IP Model, addressing, and more.
What is Data Communication?
Data communication refers to the process of transmitting and receiving data between two or more devices over a communication channel. It involves the conversion of data into signals that can be transmitted and then decoding those signals at the receiving end. Effective data communication requires the use of appropriate protocols, encoding techniques, and hardware devices.
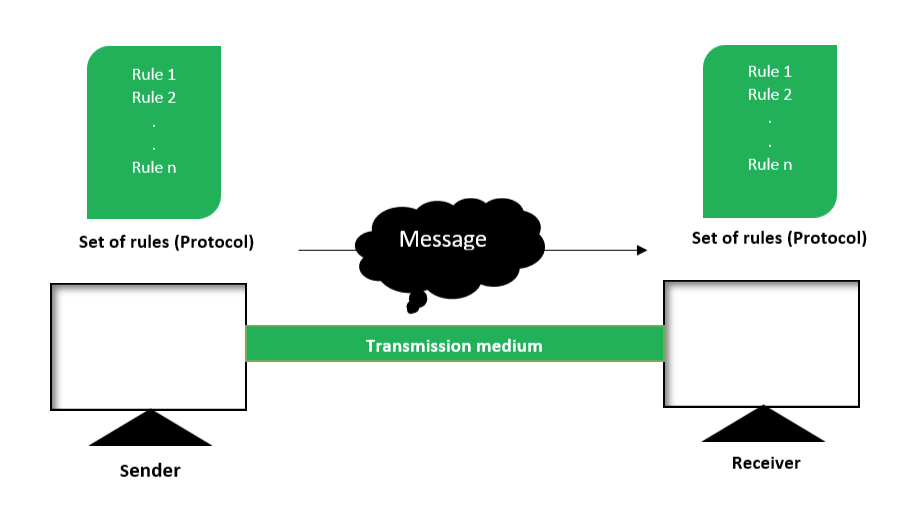
Components of Data Communication
Data communication systems consist of several components that work together to enable the transfer of data. These components include:
- Sender: The device or system that initiates the data transmission.
- Receiver: The device or system that receives the transmitted data.
- Medium/Channel: The physical pathway through which data is transmitted, such as cables or wireless connections.
- Protocol: A set of rules and conventions that govern the transmission and reception of data.
- Modem: Short for modulator-demodulator, a device that converts digital signals into analog signals for transmission and vice versa.
Types of Data Transmission
Data transmission can occur in two primary ways:
- Serial Transmission: In serial transmission, data is transmitted bit by bit over a single communication channel. It is commonly used for long-distance communication and is more reliable but slower compared to parallel transmission.
- Parallel Transmission: In parallel transmission, multiple bits are transmitted simultaneously over separate communication channels. It allows for faster data transfer but is more susceptible to errors in long-distance transmissions.
Table of Content – Data Communication
Basics of Data Communication
- Data Communication – Definition, Components, Types, Channels
- Network Criteria
- Physical Structures
- Network Models
- Transmission Modes
- Difference between Serial and Parallel Transmission
- How Data Encapsulation & De-encapsulation Works?
OSI Model
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
TCP/IP Model
- TCP/IP Model
- Application Layer in TCP/IP
- Transport Layer in TCP/IP
- Internet Layer in the TCP/IP Model
- Physical Layer in TCP/IP
- Difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model
Addressing
- Physical Addresses
- Logical Addresses
- Port Addresses
- Specific Addresses
Data and Signals
- Analog and Digital Signals
- Composite Signals
- Periodic and Nonperiodic Signals
- Time and Frequency Domains
- Difference between Bit Rate and Baud Rate
Transmission of Signals
- What is Data Transmission.
- TRANSMISSION IMPAIRMENT
- Noiseless Channel: Nyquist Bit Rate
- Noisy Channel: Shannon Capacity
- What is Bandwidth? Definition, Working, Importance, Uses
- DIGITAL-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
- Line Coding
- ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
- Delta Modulation (DM)
- DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
- Aspects of Digital-to-Analog Conversion
- Amplitude Shift Keying
- Frequency Shift Keying
- Phase Shift Keying
- Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
- ANALOG-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
- Modulation and its type
Multiplexing
- Multiplexing
- Types of Multiplexing in Data Communications
- Frequency-Division Multiplexing
- Wavelength-Division Multiplexing
- Synchronous Time-Division Multiplexing
- Statistical Time-Division Multiplexing
- Difference between FDM,TDM and WDM
Transmission Media
- Types of Transmission Media
- GUIDED MEDIA
- Twisted-Pair Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Fiber-Optic Cable
- Difference between Twisted pair cable, Co-axial cable and Optical fiber cable
- UNGUIDED MEDIA
- Radio Waves
- Microwaves Transmission System
- Infrared Signals
- Difference between Guided and Unguided Media
Error Detection and Correction
- Types of Errors
- Error Detection
- Forward Error Correction Versus Retransmission
- Parity Check
- Vertical Redundancy Check (VRC)
- Longitudinal Redundancy Check (LRC)/2-D Parity Check
- CRC( Cyclic Redundancy Check)
- Error Correction
- Hamming Code
- Hamming Distance
- Minimum Hamming Distance
- CHECKSUM
Channelization
- Frequency-Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- Ethernet
- Bridged Ethernet
- Switched Ethernet
- Full-Duplex Ethernet
- FAST ETHERNET
- GIGABIT ETHERNET
Logical Addressing
- Classful Addressing
- Classless Addressing
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Security
- Introduction to Cryptography
- Substitution Ciphers
- Transposition Ciphers
- One-Time Pads
- SYMMETRIC-KEY ALGORITHMS
- DES—The Data Encryption Standard
- AES—The Advanced Encryption Standard
- Cipher Modes
- PUBLIC-KEY ALGORITHMS
- RSA
- DIGITAL SIGNATURES
- Public-Key Signatures
- Message Digests
- The Birthday Attack
- IPsec
- Virtual Private Networks
- Wireless Security
- The Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
- EMAIL SECURITY
- PGP—Pretty Good Privacy
Applications of Data Communication
Computer systems and other devices are connected to form a network. They provide numerous advantages:
- Video conferences
- Parallel computing
- Resource sharing such as printers and storage devices
- Exchange of information by means of e-Mails and FTP
- Information sharing by using the Web or the Internet
- Interaction with other users using dynamic web pages
- IP phones
- Instant messaging
FAQs on Data Communication
Q.1 What is the importance of data communication?
Data communication is important for connecting devices and for the transfer of information in the digital world and various technologies and services we dependent in daily life.
Q.2 How does data transmission occur?
Data transmission occurs through various mediums such as cables, wireless connections, or optical fibers. The data is encoded, transmitted, received, and decoded using protocols and devices.
Q.3 What are the benefits of wireless data communication?
Wireless data communication provides mobility, flexibility, and convenience. It allows devices to connect and communicate without the limitations of physical cables.
Q.4 How does data communication ensure security?
Data communication provide encryption, authentication, and other security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, interception, and tampering.


